Den Den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed (EAA) er et vigtigt skridt i retning af at skabe et mere inkluderende digitalt og fysisk miljø i hele EU. Loven er designet til at sikre, at mennesker med handicap har lige adgang til vigtige produkter og tjenester, og den opstiller klare tilgængelighedskrav til virksomheder, der opererer på EU-markedet. Med et bredt anvendelsesområde, der dækker digitale platforme, fysiske produkter og kommunikationstjenester, påvirker EAA mange brancher og kræver proaktiv overholdelse. At forstå disse krav er afgørende for, at virksomheder kan udvise socialt ansvar og undgå juridiske risici i en stadig mere tilgængelighedsbevidst verden.
Oversigt over den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed
Den europæiske tilgængelighedslov har til formål at harmonisere tilgængelighedskravene på tværs af EU's medlemslande ved at fastsætte fælles standarder for produkter og tjenester. Dens primære formål er at fjerne barrierer for mennesker med handicap og sikre, at de kan deltage fuldt ud i samfundet og økonomien. Loven dækker en bred vifte af produkter og tjenester og fastsætter minimumskriterier for tilgængelighed, som skal opfyldes af producenter, tjenesteudbydere og sælgere.
Produkter og tjenester, der er omfattet af EAA, omfatter digitale produkter som hjemmesider, mobilapps, e-handelsplatforme og software samt fysiske produkter som pengeautomater, billetautomater, e-læsere og banktjenester. Dette brede anvendelsesområde afspejler lovens mål om at fremme et inkluderende digitalt indre marked, hvor tilgængelighed er et lovkrav snarere end blot en mulighed.
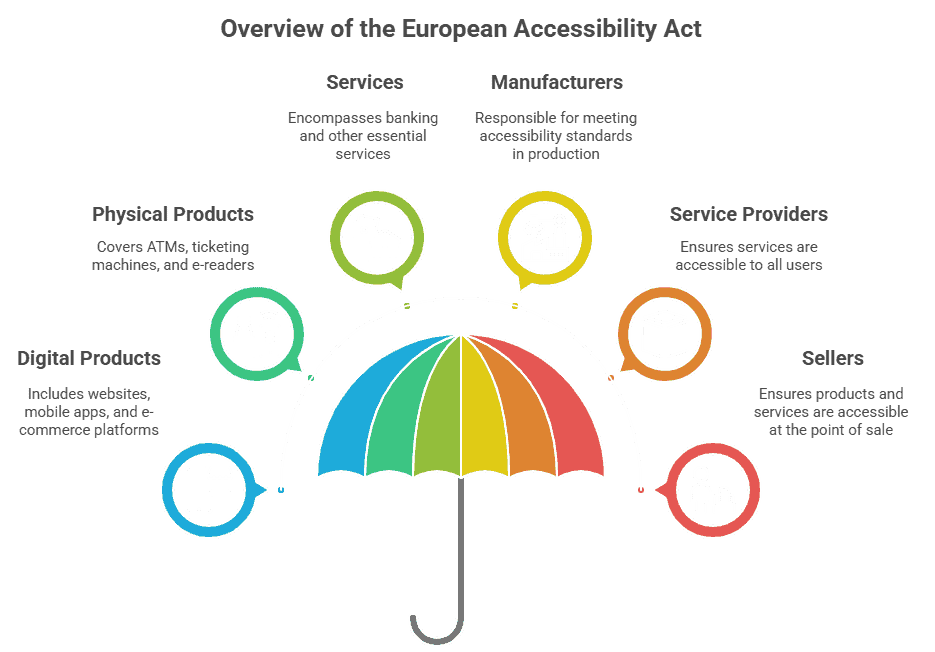
Hvem skal overholde reglerne og hvornår?
EAA gælder for virksomheder og organisationer, der leverer produkter eller tjenester inden for EU, herunder dem, der er baseret uden for EU, men sælger til dets marked. De berørte nøglesektorer omfatter e-handel, transport, bank- og finanstjenester, telekommunikation og udbydere af digitalt indhold. I bund og grund skal enhver virksomhed, der tilbyder varer eller tjenester til forbrugere i EU, vurdere sine tilgængelighedsforpligtelser i henhold til loven.
Fristerne for overholdelse varierer afhængigt af produkt- eller servicekategorien, men kræver generelt, at virksomheder opfylder lovens tilgængelighedsstandarder inden den 28. juni 2025. Virksomheder, der udskyder fristen, risikerer at blive udsat for juridiske udfordringer og skade deres omdømme som følge heraf.
Vigtigste krav til tilgængelighed
Den europæiske tilgængelighedslov (EAA) opstiller specifikke krav for at gøre produkter, tjenester og kommunikation tilgængelige for mennesker med handicap. Disse krav dækker digitale løsninger, fysiske miljøer og informationslevering og sikrer, at tilgængelighed er indbygget i enhver interaktion.
Digitale produkter og tjenester
Digital tilgængelighed er et kernefokus for EAA. Virksomheder skal sikre, at hjemmesider, mobilapplikationer og softwareprodukter er tilgængelige for brugere med handicap. Dette omfatter overholdelse af Retningslinjer for tilgængelighed af webindhold (WCAG), som dækker aspekter som tastaturnavigation, skærmlæserkompatibilitet, alternativ tekst til billeder og tilstrækkelig farvekontrast. Digitale produkter skal også understøtte hjælpeteknologier og give tilgængelige brugergrænseflader.
Overvejelser om det byggede miljø
Loven omhandler også tilgængelighed i det byggede miljø i forbindelse med produkter og tjenester som f.eks. pengeautomater, billetmaskiner og selvbetjeningsterminaler. Disse fysiske produkter skal designes, så de kan bruges af mennesker med forskellige handicap, herunder mennesker med bevægelses-, syns- eller hørenedsættelse. Funktioner som taktile knapper og lydoutput er eksempler på nødvendige tilgængelighedstilpasninger.
Tilgængelighed til information og kommunikation
Effektiv kommunikation er afgørende for tilgængelighed. EAA kræver, at information, der leveres gennem produkter og tjenester, er tilgængelig, herunder instruktioner, kundesupport og digitalt indhold. Det betyder, at der skal leveres tilgængelige formater som f.eks. letlæselig tekst, undertekster til videoer og tegnsprogstolkning, hvor det er relevant. Kommunikationskanaler skal kunne bruges af mennesker med forskellige handicap for at sikre lige adgang.
Vigtige forskelle fra andre tilgængelighedslove
Den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed (EAA) adskiller sig fra andre rammer for tilgængelighed ved at kombinere digitale og fysiske krav under et enkelt EU-dækkende mandat. Mens globale retningslinjer og nationale love som WCAG, ADA og Section 508 påvirker tilgængelighedspraksis, etablerer EAA harmoniserede standarder med klare håndhævelsesmekanismer på tværs af alle medlemslande.
Sammenligning med WCAG, ADA og Section 508
Mens WCAG giver internationalt accepterede tekniske retningslinjer for webtilgængelighed, EAA er en lovgivningsmæssig ramme, der kræver overholdelse af disse og andre standarder i hele EU. I modsætning til USA Lov om handicappede amerikanere (ADA), som gælder bredt for offentlig indkvartering og er blevet fortolket til at omfatte hjemmesider, er EAA specifikt rettet mod digitale og fysiske produkter med klare deadlines for overholdelse. Afsnit 508 i USA gælder for føderale agenturer og entreprenører, mens EAA gælder i hele EU for både den offentlige og den private sektor.
Unikke krav i hele EU
EAA's harmoniserede tilgang sikrer ensartede tilgængelighedsstandarder på tværs af alle EU's medlemslande, hvilket reducerer fragmentering og forenkler overholdelsen for virksomheder, der opererer i flere lande. Den strækker sig også ud over digital tilgængelighed og omfatter fysiske produkter og tjenester, hvilket afspejler et omfattende syn på tilgængelighed. Loven indfører markedsovervågningsmekanismer og sanktioner for manglende overholdelse og lægger vægt på håndhævelse på EU-plan.
Almindelige compliance-udfordringer for virksomheder
At opfylde kravene i den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed udgør ofte praktiske forhindringer for organisationer. Virksomheder skal opdatere eksisterende produkter, integrere tilgængelighed i udviklingsarbejdsgange og koordinere overholdelse på tværs af flere markeder. Disse udfordringer understreger behovet for strategisk planlægning, investering og langsigtet engagement i tilgængelighed.
Tilpasning af eksisterende produkter og tjenester
Mange virksomheder står over for udfordringer med at opdatere ældre produkter og digitale platforme, så de opfylder EAA's krav. Eftermontering af tilgængelighedsfunktioner kan være kompleks og dyr, især for fysiske produkter med lange udviklingscyklusser. Prioritering af opdateringer og investering i tilgængeligt design fra begyndelsen mindsker disse udfordringer.
Integrering af tilgængelighed i udviklingsprocesser
Indarbejdelse af tilgængelighed i produktudviklingens livscyklus kræver kulturelle og proceduremæssige ændringer. Teams skal uddannes i tilgængelighedsprincipper, og test skal integreres fra design til implementering. Uden denne integration kan tilgængelighed blive overset eller kun behandlet som en eftertanke.
Håndtering af compliance på tværs af landegrænser
Virksomheder, der opererer på tværs af flere EU-lande, skal navigere i forskellige nationale implementeringer og håndhævelsespraksisser. Det er vigtigt at koordinere indsatsen for at overholde reglerne og holde sig orienteret om regionale nuancer for at undgå juridiske risici og sikre ensartet tilgængelighed.
Sådan tjekker du, om din virksomhed lever op til standarderne
Verifikation af overholdelse af den europæiske tilgængelighedslov kræver både intern og ekstern evaluering. En blanding af revisioner, tredjepartsvurderinger og test med hjælpemidler giver et omfattende overblik over tilgængeligheden og sikrer, at produkter og tjenester lever op til de juridiske standarder og giver reel brugbarhed for mennesker med handicap.
Interne tilgængelighedsrevisioner
Regelmæssige interne audits hjælper organisationer med at identificere huller i tilgængeligheden i produkter og tjenester. Disse revisioner gennemgår design, indhold og funktionalitet i forhold til EAA-kriterier og WCAG-retningslinjer, hvilket giver et grundlag for afhjælpning.
Tredjepartsvurderinger af tilgængelighed
Ved at inddrage eksterne eksperter får man en objektiv vurdering af, om tilgængeligheden overholdes. Tredjepartsvurderinger kan afdække problemer, som måske er blevet overset internt, og give certificering eller dokumentation, der understøtter lovkrav.
Test med hjælpemidler
Test med skærmlæsere, forstørrelsesglas, stemmegenkendelsessoftware og andre hjælpemidler sikrer, at produkter og tjenester virkelig kan bruges af mennesker med handicap. Denne test validerer teknisk overensstemmelse og brugeroplevelse.
Skridt til at opnå overensstemmelse
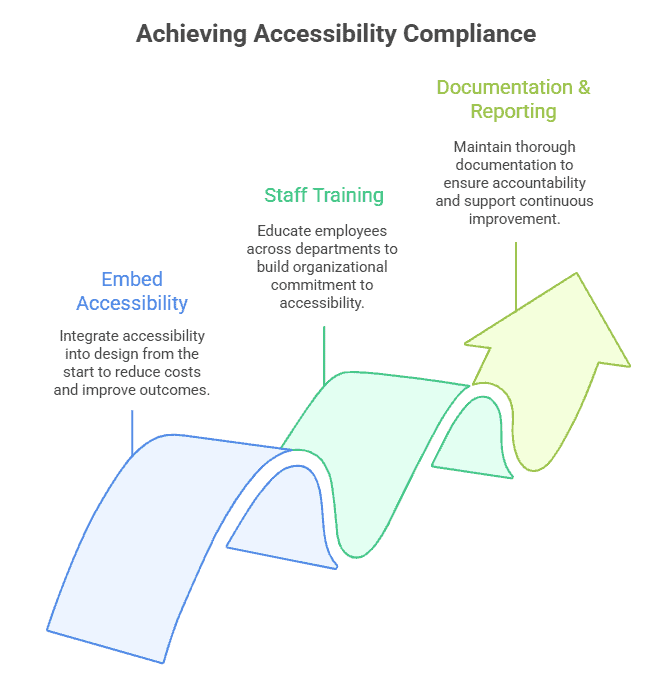
Overholdelse af den europæiske tilgængelighedslov kræver en struktureret tilgang, der integrerer tilgængelighed i alle faser af forretningsdriften. Fra inkluderende design og uddannelse af personale til opretholdelse af klar dokumentation hjælper disse trin organisationer med at opfylde juridiske forpligtelser og samtidig levere lige adgang til alle brugere.
Integrering af tilgængelighed fra starten
At tænke tilgængelighed ind i produkter og tjenester fra starten reducerer omkostningerne og forbedrer resultaterne. Nøglestrategier er at bruge inkluderende designprincipper, følge WCAG-standarder og involvere brugere med handicap i test.
Træning og bevidstgørelse af personale
At uddanne medarbejdere på tværs af afdelinger om tilgængelighedskrav skaber organisatorisk engagement. Uddannelse sikrer, at designere, udviklere, marketingfolk og kundeservicemedarbejdere forstår deres rolle i at opretholde compliance.
Dokumentation og rapportering
Vedligeholdelse af grundig dokumentation af tilgængelighedspolitikker, designbeslutninger, testresultater og afhjælpningstiltag sikrer ansvarlighed. Gennemsigtig rapportering understøtter verificering af overholdelse og løbende forbedringer.
Fordele ved at opfylde den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed
Overholdelse af den europæiske tilgængelighedslov giver fordele, der går ud over de juridiske forpligtelser. Virksomheder, der prioriterer tilgængelighed, kan udvide deres kundebase, styrke brandets omdømme og mindske risikoen for sanktioner eller afbrydelser. Disse fordele placerer tilgængelighed som både et lovkrav og en strategisk mulighed.
Større rækkevidde på markedet
Tilgængelige produkter og tjenester åbner døre for millioner af mennesker med handicap i hele EU. Dette udvidede publikum repræsenterer betydelige kommercielle muligheder.
Forbedret brand-omdømme
At demonstrere en forpligtelse til tilgængelighed styrker brandets image og opbygger tillid hos forbrugere, partnere og myndigheder. Inkluderende virksomheder opfattes som socialt ansvarlige og fremsynede.
Reduceret juridisk og operationel risiko
Overholdelse af EAA minimerer risikoen for retssager, bøder og skader på omdømmet. Proaktiv tilgængelighed reducerer driftsforstyrrelser betydeligt og understøtter bæredygtig forretningspraksis.
Løbende overholdelse og overvågning
Overholdelse af den europæiske tilgængelighedslov kræver regelmæssig gennemgang og opdatering af produkter, tjenester og interne processer. Tilgængelighedsstandarder og -teknologier udvikler sig, så virksomheder skal holde sig informeret og tilpasse sig i overensstemmelse hermed. Overvågning af den juridiske udvikling og deltagelse i branchefora hjælper organisationer med at forudse ændringer og bevare lederskabet inden for digital tilgængelighed.
Byg en inkluderende fremtid med den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed
Den europæiske lov om tilgængelighed viser en klar vej mod et mere inkluderende og tilgængeligt marked i hele EU. Ved at forstå kravene og handle proaktivt kan virksomheder ikke kun opfylde juridiske forpligtelser, men også åbne op for nye vækstmuligheder og forbedre brugeroplevelsen. Ressourcer som f.eks. officiel EU-vejledning giver værdifuld støtte til organisationer, der navigerer i compliance. At tilslutte sig EAA er en strategisk investering i tilgængelighed, innovation og socialt ansvar.
